Squaraine Rotaxanes
Squaraine rotaxanes are mechanically interlocked molecules comprised of a squaraine dye and a tetralactam macromolecule [41].
General structure of SeTau squaraine rotaxanes and available product categories
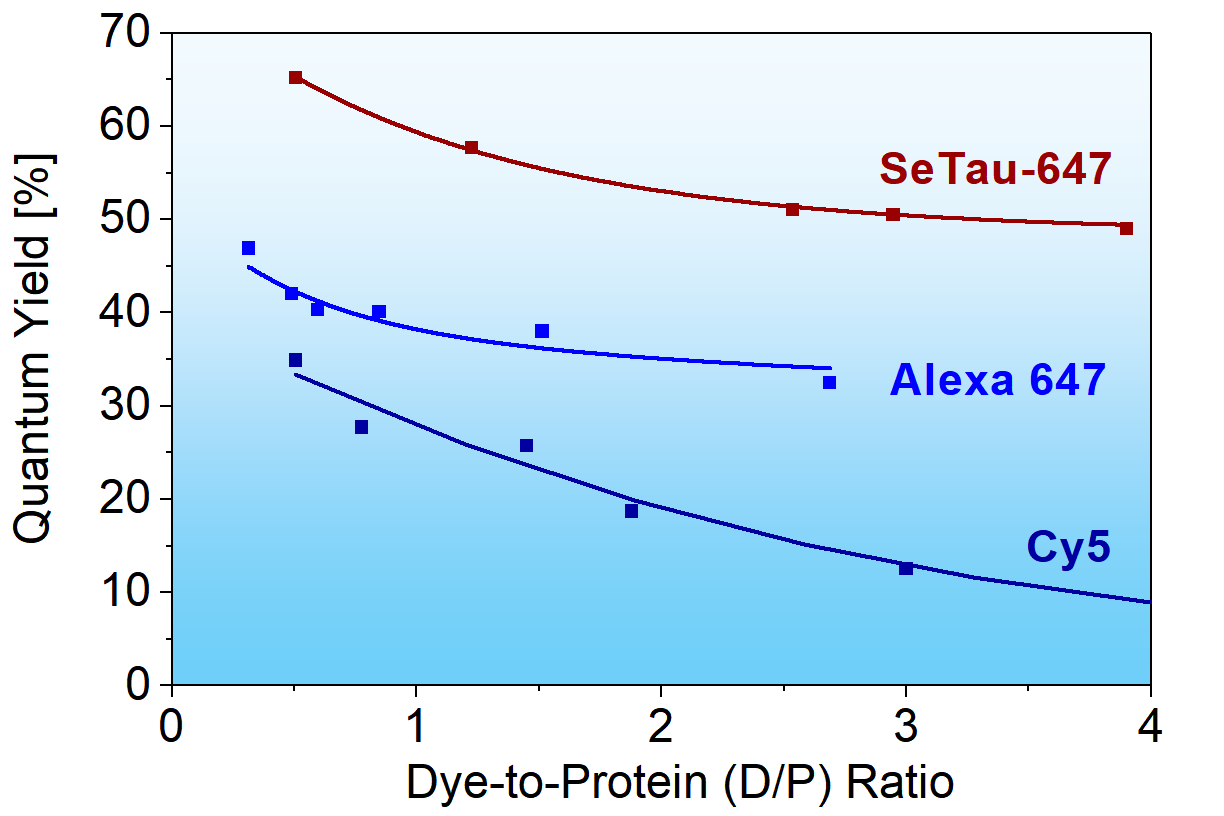
SETA BioMedicals developed water-soluble, ionic squaraine rotaxanes to overcome some of the shortcomings of conventional fluorescent dyes. Ionic squaraine rotaxanes combine several highly desirable properties of fluorescent reporters: extremely high quantum yields in aqueous buffers (up to 65%), high extinction coefficients (up to 295,000 M-1cm-1), very high photostability, large Stokes' shifts (up to 50 nm), and low sensitivity towards oxygen species.
Due to their very high chemical stability, particularly against oxidative reagents such as peroxides or ozone (see below), our squaraine rotaxanes are excellent detection reagents for use in microarrays. For more detailed information, please refer to the DNA and protein microarrays page.
The photobleaching rates of 13 fluorescent dyes, four of which were conjugated to trolox, were investigated for single-molecule measurements at 37°C in living cells. For this purpose, they were linked to a tag protein that was fused to CD47. In this study, SeTau-647 (K9-4149 or K9-4148) exhibited the best photobleaching performance with an exponential lifetime of 105.8 sec, which is the longest single fluorescent molecular tracking ever reported [32].
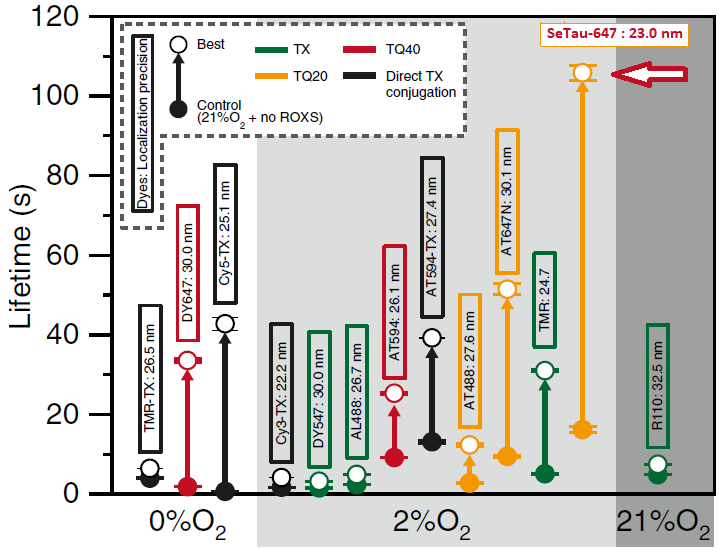
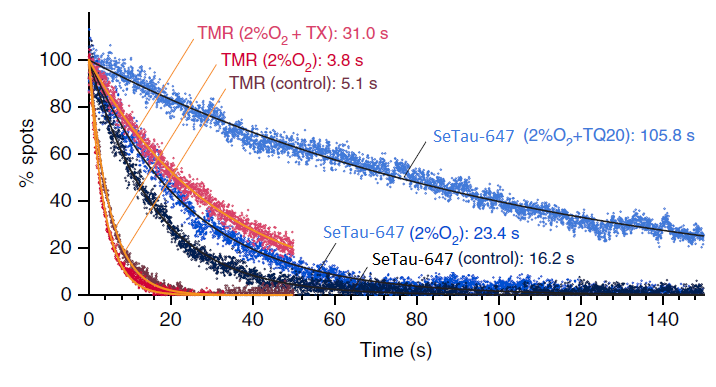
found in each 33-ms frame for TMR and SeTau-647 (K9-4148) [32]
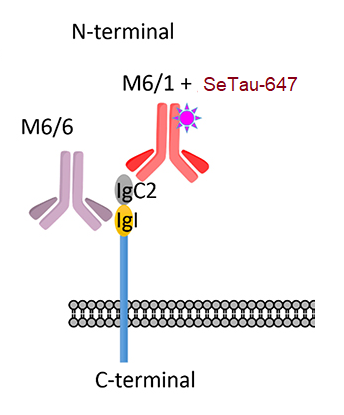
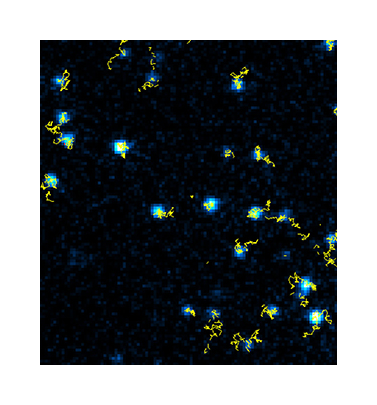
SeTau-647 (K9-4149) was recently used in the investigation of the cellular dynamics and mobility of the type IV pilus receptor CD-147 upon treatment with pili-enriched fractions and specific antibodies [34]. Using SeTau-647 (K9-4149)-labeled MEM-6/1 antibodies, the researchers tracked CD-147 on the basal plasma membrane of human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMEC) for 100 s with a time resolution of 20 ms using TIRF microscopy.
Excitation Light Sources
Characteristics
Product Number
(Specs Sheet)Product Name
(Product Info)Target Group
380
405
436
488
532
594
635
650
680
700
750
780
Medium
λ abs
[nm]ε
[M –1
cm–1]λ em
[nm]QY
[%]FLT
[ns]Buy
K9-4119
SeTau-665-NHS
NH2
•
•
PB 7.4
664
160,000
712
53
3.1
K9-4142
SeTau-647-di-NHS
NH2
•
•
PB 7.4
650
200,000
694
65
3.2
K9-4145
SeTau-633-Ethyl-Ester
•
•
CHCl3
634
105,000
683
68
K9-4148
SeTau-647-Maleimide
SH
•
•
PB 7.4
648
200,000
692
45
3.2
K9-4149
SeTau-647-NHS
NH2
•
•
PB 7.4
649
200,000
695
61
3.2
K9-4150
SeTau-647
•
•
PB 7.4
647
211,000
693
59
3.1
K9-4169
SeTau-670-NHS
NH2
•
•
•
PB 7.4
673
275,000
694
36
1.6
K9-4179
SeTau-680-NHS
NH2
•
•
•
PB 7.4
683
295,000
705
58
2.9
K9-4154
SeTau-647-DBCO
N3
•
•
PB 7.4
649
200,000
690
60
3.2
K9-3152
SeTau-488-NHS
NH2
•
PBS 7.4
486
59,000
532
27
1.2
K9-3153
new
SeTau-488-Maleimide
SH
•
PBS 7.4
484
59,000
531
14
K9-4159
new
SeTau-660-NHS
NH2
•
•
PB 7.4
663
240,000
694
50
3.36
K9-3162
new
SeTau-500-NHS
NH2
•
PB 7.4
502
59,600
567
43
2.8
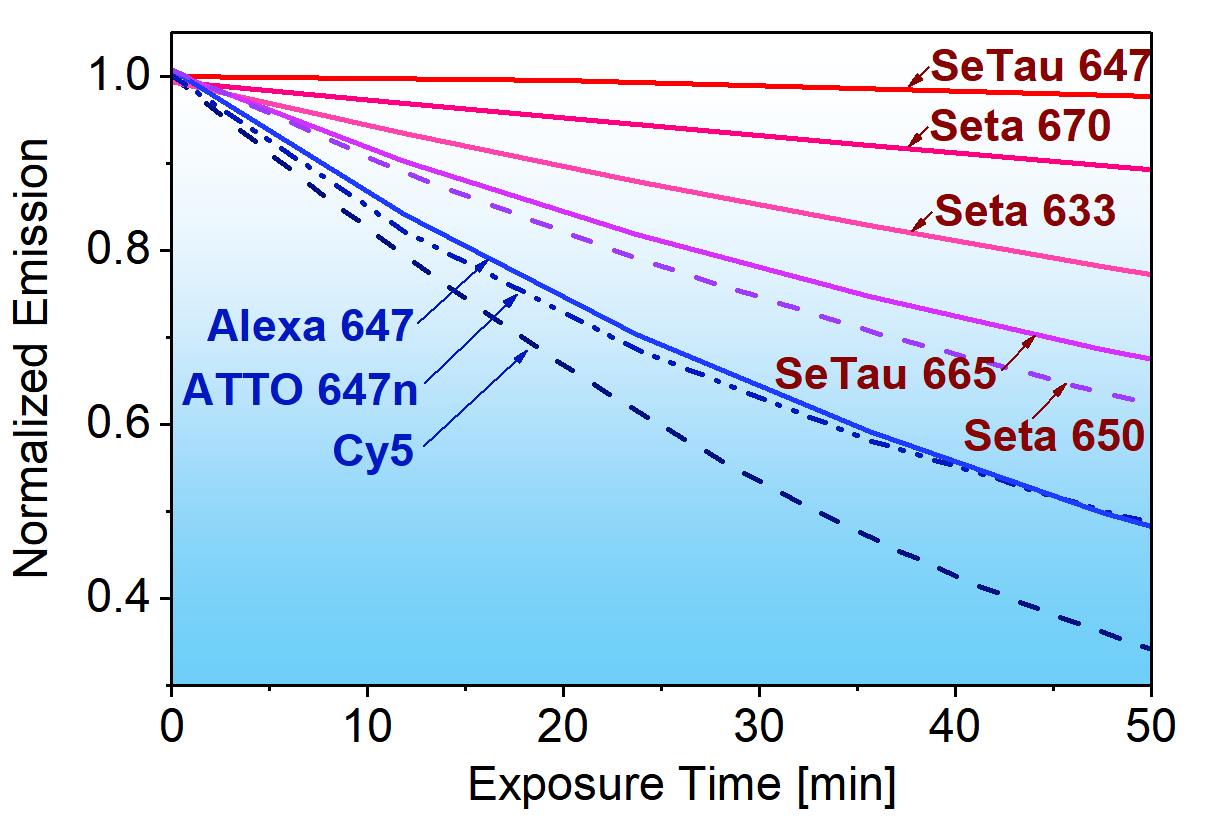
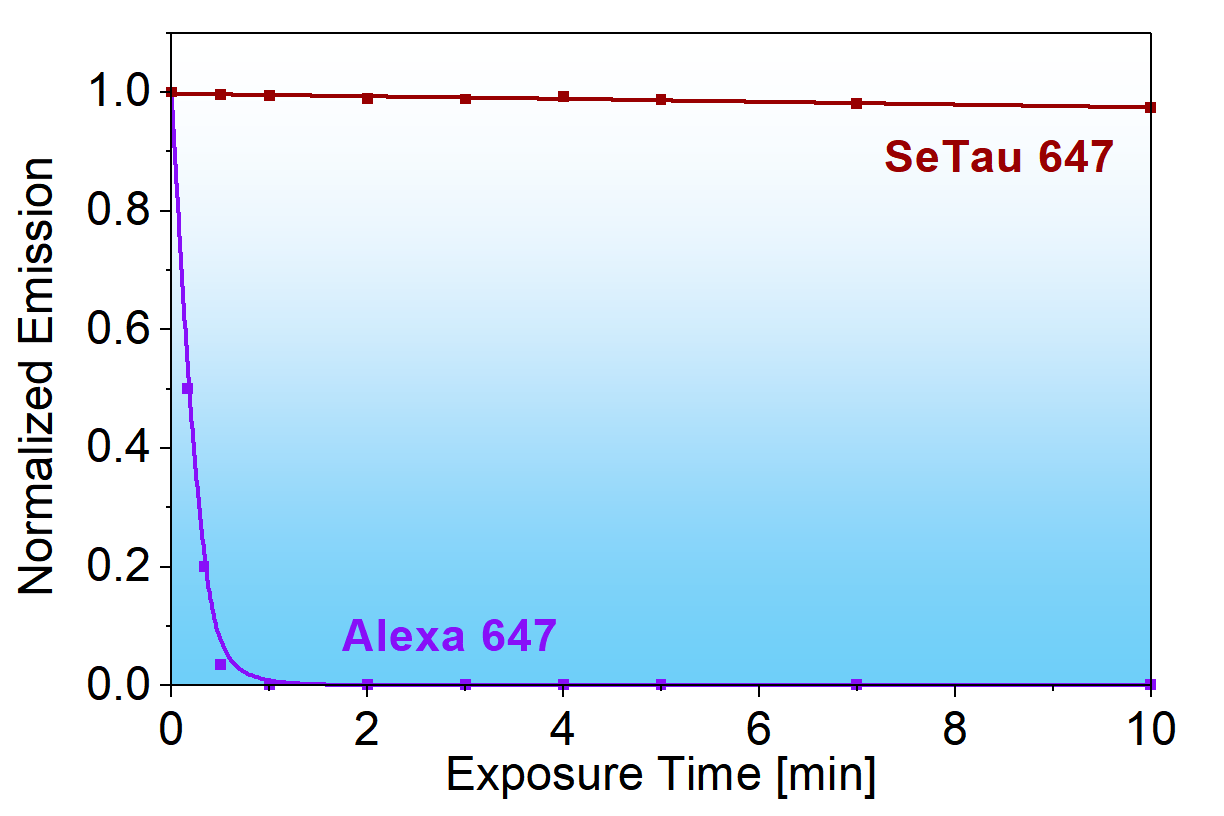
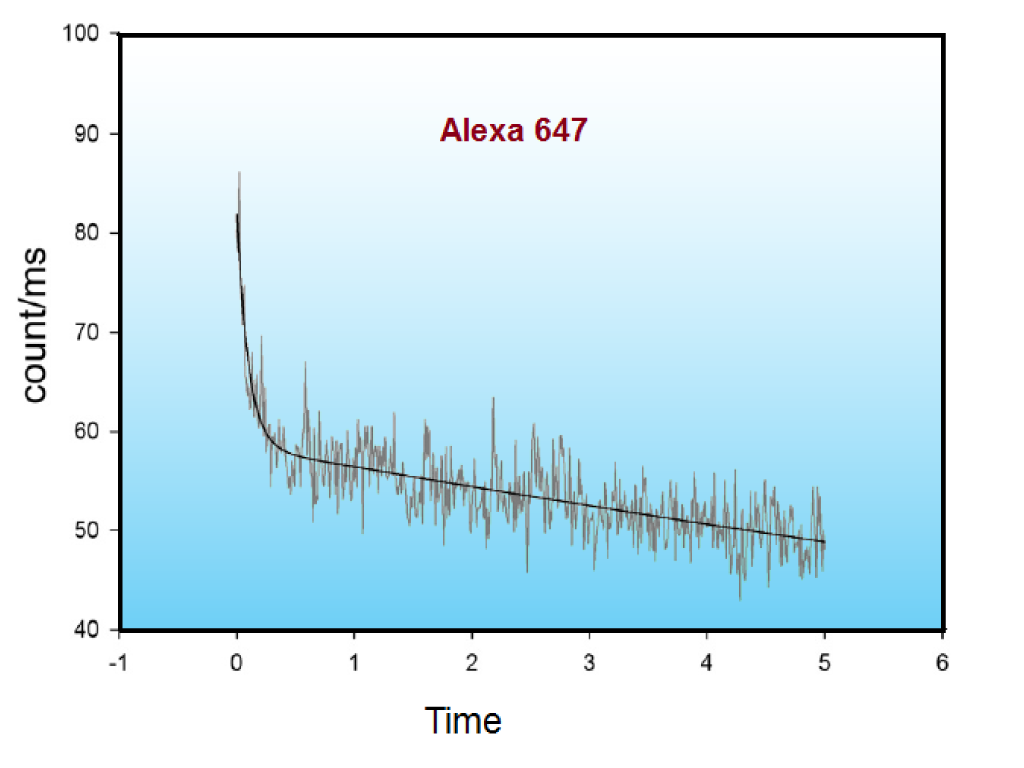
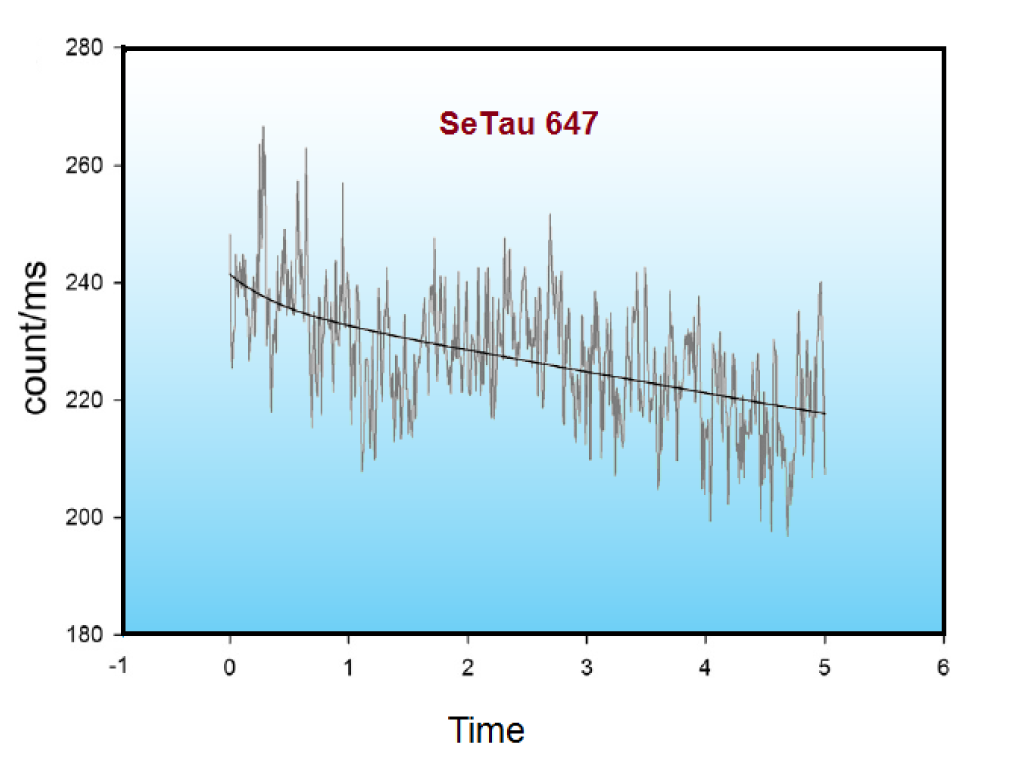
For a direct comparison of the imaging properties and characteristics of Alexa 647 and SeTau 647, we refer you to the following publication: D. Duggal et al. Degree of order and kinetics of phosphorylated (P) and de-P cross-bridges. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol (November 27, 2013): SeTau-647-maleimide (K9-4148) was chosen over Alexa 647 for the above imaging application mainly because it was more resistant to photobleaching and because it is brighter and has twice as large Stokes' shift (44 nm) compared to Alexa 647 (20 nm).
Comparison of the photobleaching of Alexa 647 (left) vs. SeTau 647 (right) at identical concentrations: the photobleaching rate for SeTau 647 was 4.2 times slower than for Alexa 647! In addition, the mean count rate of SeTau 647 was approximately 4 times higher than that of Alexa 647.
SeTau-680-NHS (Φ = 0.58, ε = 215,000 M-1cm-1, and Φ∙ε = 124,700 M-1cm-1) with a similar absorption emission as Alexa 680 is twice as bright as Alexa 680 (Φ = 0.36, ε = 183,000 M-1cm-1, and Φ∙ε = 65,880 M-1cm-1) and exhibits a lower quenching tendency when labeled to biomolecules. Exc./Em. max of IgG-conjugates: 682/703 nm.
SeTau-670-NHS (Φ = 0.36, ε = 275,000 M-1cm-1 and Φ∙ε = 99,000 M-1cm-1) with the same absorption and emission as Cy5.5 is about twice as bright as Cy5.5 (Φ∙ε = 44,850 M-1cm-1) and 1.5 as bright as Alexa 680 (Φ = 0.36, ε = 183,000 M-1cm-1 and Φ∙ε = 65,880 M-1cm-1), and exhibits a lower quenching tendency when labeled to biomolecules. Exc./Em. max of IgG-conjugates: 672/692 nm.
SeTau-665-NHS is a hydrophilic, mono-reactive squaraine rotaxane label for biomolecules. It is very bright (Φ = 0.53, ε = 161,000 M-1cm-1 and Φ∙ε = 83,330) with a large Stokes' shift of 48 nm and a similar emission as Alexa 700 (Φ = 0.25, ε = 205,000 M-1cm-1 and Φ∙ε = 51,250 M-1cm-1), but SeTau-665 is a factor of ~ 1.6 times brighter. It is optimally excited with 665 nm light sources. This dye also holds the record for 2PECSs of fluorescent labels with >8500 GM at 900 nm. Exc./Em. max of IgG-conjugates: 665/712 nm.
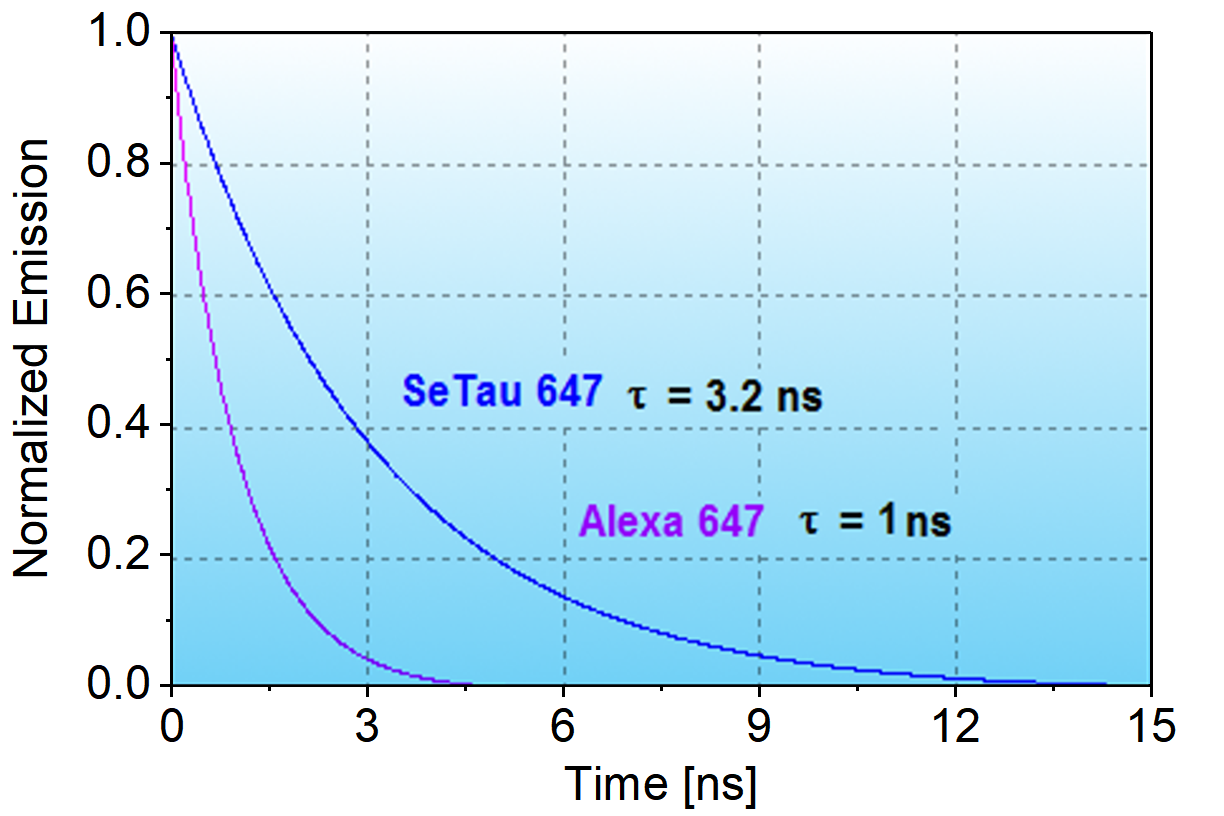
SeTau-647-NHS is a hydrophilic, mono-reactive squaraine rotaxane label for biomolecules. Compared to Cy5 (Φ = 0.27, ε = 250,000 M-1cm-1 and Φ∙ε = 67,500 M-1cm-1) or Alexa 647 (Φ = 0.33, ε = 239,000 M-1cm-1 and Φ∙ε = 78,870 M-1cm-1), it is an extremely bright label (Φ = 0.53, ε = 200,000 M-1cm-1 and Φ∙ε = 106,000 M-1cm-1) with a large Stokes' shift of 46 nm. It is a highly ozone- and photo-stable dye that is optimally excited with the 647 nm light sources. Exc./Em. max for conjugates: 649/695 nm.
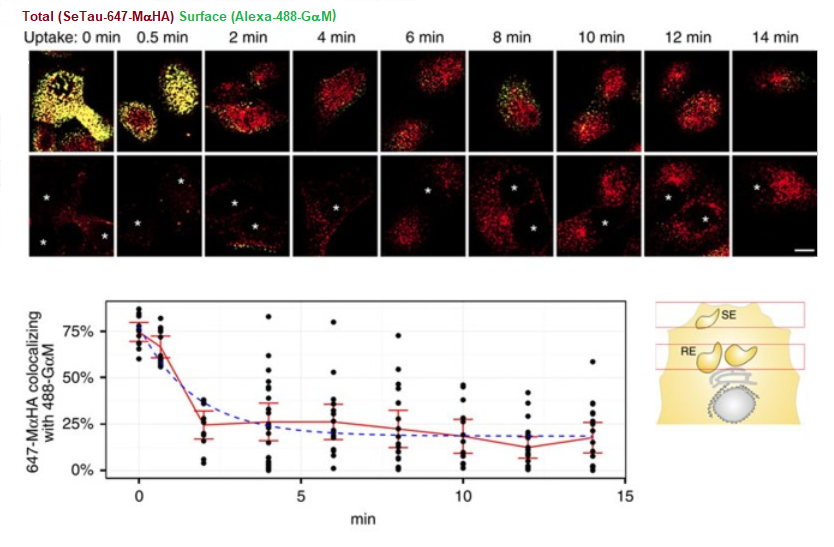
SeTau 647 was used by several research groups at highly reputed universities e.g. at Harvard Medical School where the authors compared 3 imaging probes labeled with Alexa 488, Alexa 568 and SeTau 647 and concluded that SeTau-647 has near ideal in vivo imaging characteristics and at the Weill Medical College of Cornell University where quantitative live-imaging with SeTau-647 (K9-4149) and mathematical modelling was used to outline the recycling pathway of the Megalin (LRP-2) receptor in MDCK cells (see below and in Nature Comm. 2016, DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11550).
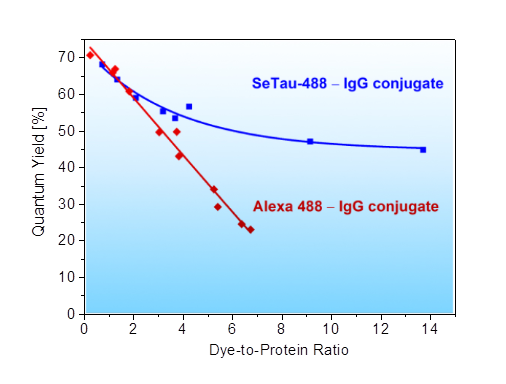
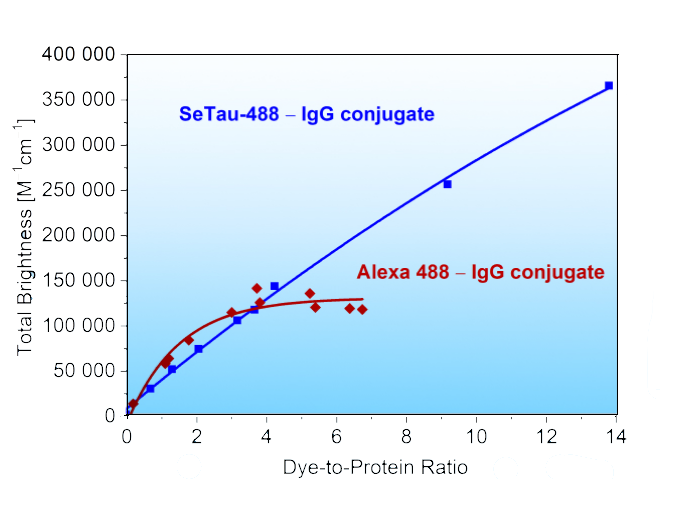
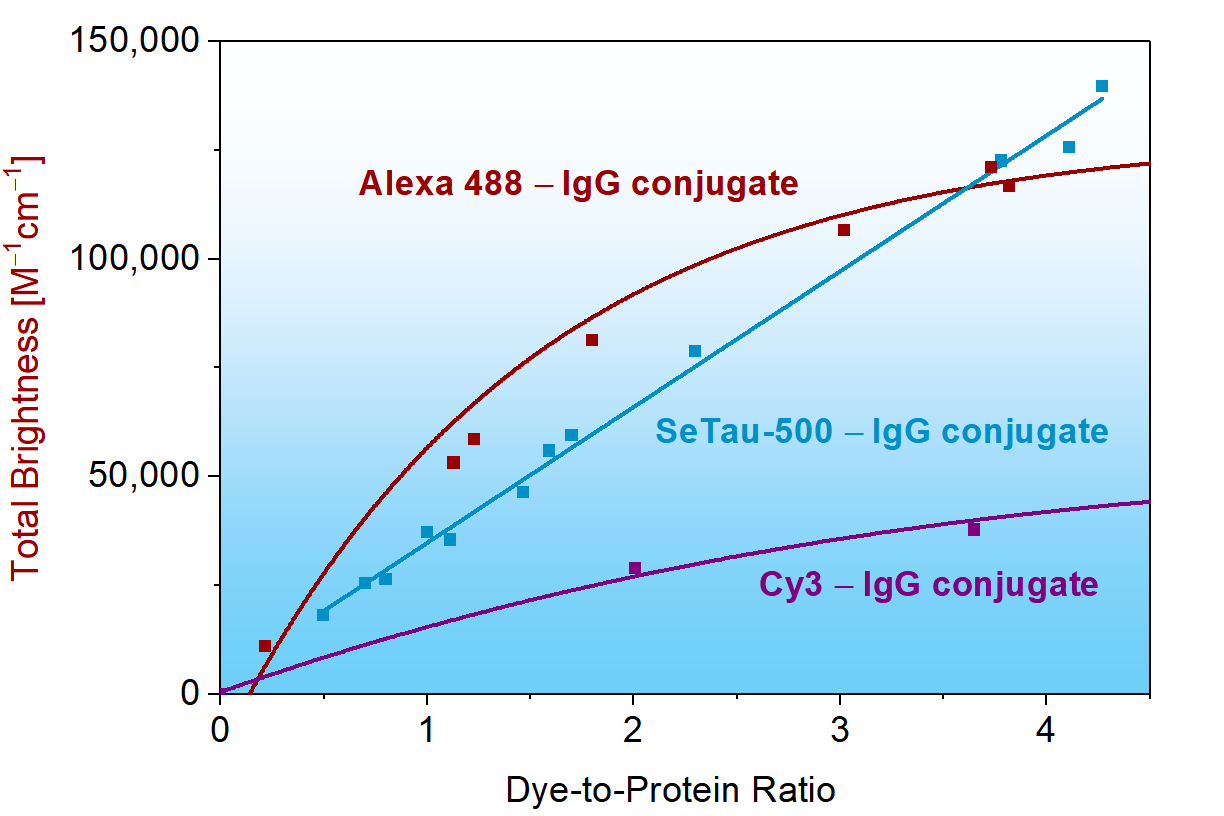
as compared to Alexa 488 — IgG and Cy3 — IgG conjugates
SeTau-488-NHS (Φ = 0.27, ε = 59,000 M-1cm-1 and Φ∙ε = 15,930 M-1cm-1), which has absorption and emission characteristics similar to Alexa 488 (Φ = 0.92, ε = 73,000 M-1cm-1 and Φ∙ε = 67,160 M-1cm-1), exhibits lower brightness as a free dye. However, its brightness increases significantly upon conjugation to biomolecules, becoming an almost unquenchable fluorophore when attached to an antibody (see below and specs sheet). Exc./Em. max of IgG-conjugates: 486/532 nm.
Squaraine Rotaxanes for fluorescence lifetime, fluorescence polarization, and imaging applications
The longer lifetimes in the order of 2 - 4 ns (see below), and larger Stokes' shifts (40 - 50 nm) of squaraine rotaxanes, compared to conventional cyanine-based NIR labels (τ = 0.5 – 1.5 ns), make them in particular suitable as labels for use in fluorescence polarization immunoassays.
Squaraine rotaxanes have unique properties for 2P imaging applications with two-photon action cross sections (2PACS) in the order of up to 10,000 GM: see (K. Podgorski et al. Ultra-bright and -stable red and NIR squaraine fluorophores for in vivo two-photon imaging. PLoS ONE 7(12): e51980).
Squaraine Rotaxane imaging probes for live and fixed cells
Our fluorescent rotaxane probes exhibit exceptionally high chemical and photostability, making them ideal for imaging applications. They also possess extremely high 2-photon action cross sections, on the order of several thousand GM.
SeTau-633 is a carboxylic acid ethyl ester derivative that passively penetrates cell membranes. Once inside, these residues are hydrolyzed by esterases, thereby forming carboxyl groups that are cell-impermeable.
SeTau-647 is a highly water-soluble fluorescent probe with several negative charges and, therefore, will not passively penetrate the cell membrane. This probe is very photostable and has a quantum yield of 60% in water.
Reactive versions (NHS-ester-, maleimide-, and DBCO-derivatives) are also available for covalent attachment to various biomolecules, enabling targeted location for in vitro and in vivo optical imaging. Images can be obtained with these labeled samples for hundreds of hours!


.jpg)